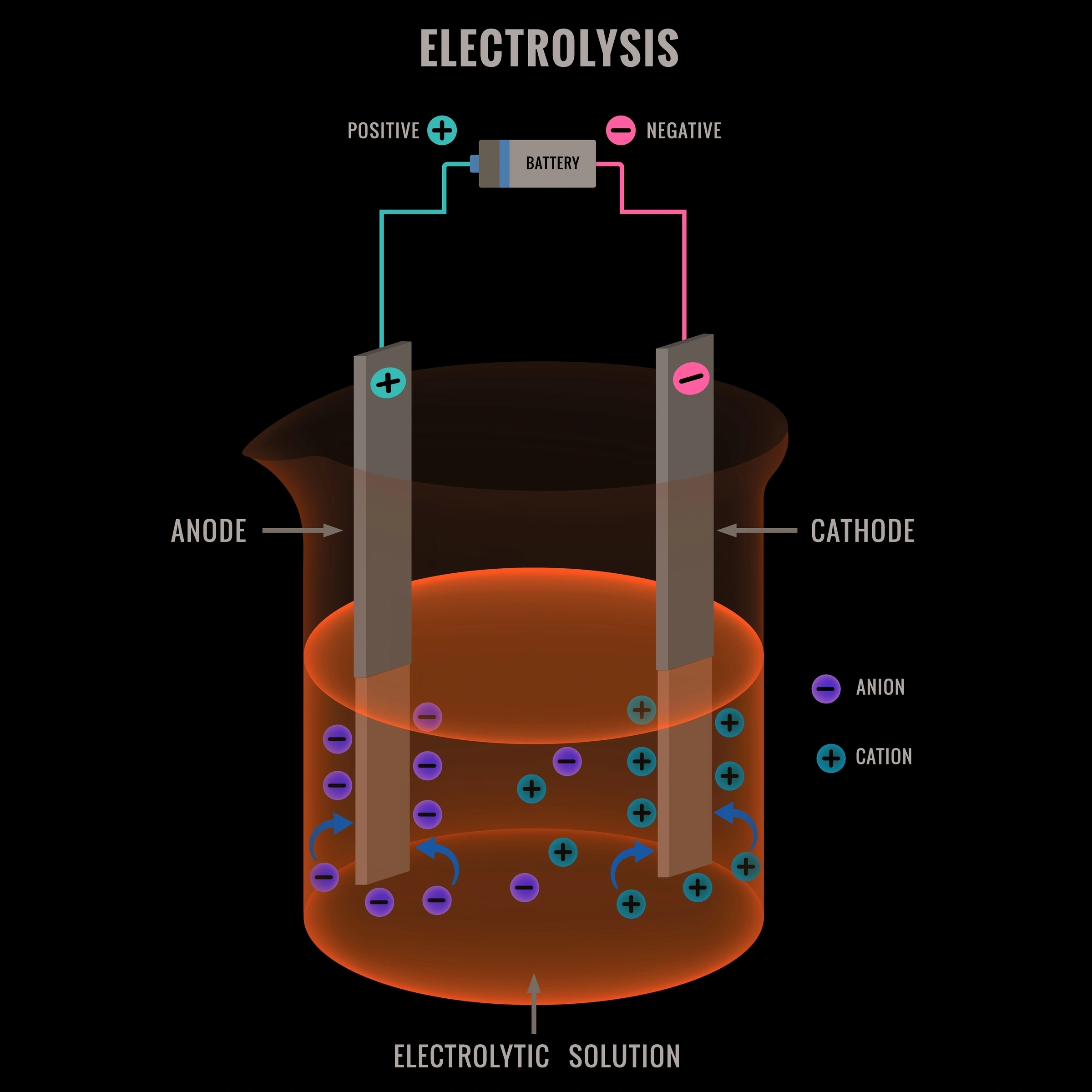
When aqueous sodium chloride (brine) is electrolyzed:
- Cathode (Reduction): \( 2\text{H}_2\text{O} + 2e^- \rightarrow \text{H}_2 + 2\text{OH}^- \)
- Anode (Oxidation): \( 2\text{Cl}^- \rightarrow \text{Cl}_2 + 2e^- \)
At the cathode, although sodium ions (\( \text{Na}^+ \)) are present, water is more easily reduced than sodium. That is because the reduction potential of water is higher than that of sodium, making water reaction more themordinamically favourable. This is a rule that always holds and should always be used when determining the species being reduced/oxidized. Water molecules gain electrons to form hydrogen gas and hydroxide ions. Thus, hydrogen gas is released at the cathode.
At the anode, chloride ions are preferentially oxidized over water. The oxidation potential of chlorine is higher than that of water (the reduction potential is lower). Chloride ions lose electrons to form chlorine gas. Thus, chlorine gas is released at the anode.
Products: Hydrogen gas at the cathode, chlorine gas at the anode, and sodium hydroxide (\( \text{NaOH} \)) remains in solution.