Electronegativity (nonmetallic character)
Electronegativity is a measure of the attraction an atom has for bonding electrons or how badly the atom wants another electron. The higher the electronegativity, the more desperate for an electron the atom is.
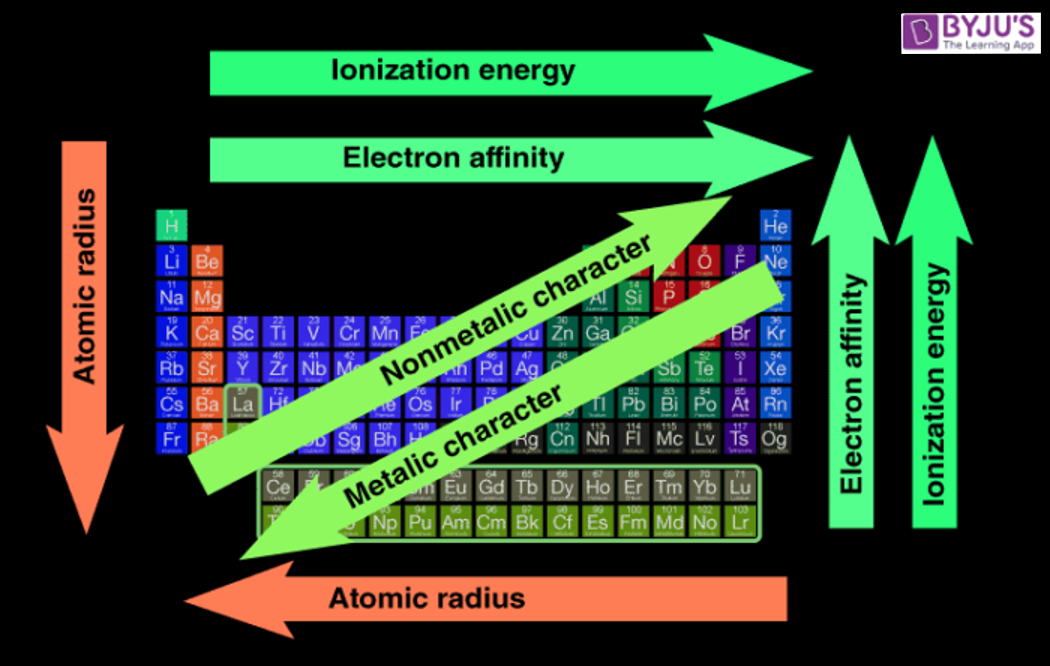
- Electronegativity increases from left to right across a period.
- The closer the valence shell is to full, the stronger the pull of that atom on the electrons in a bonding pair. Electronegativity decreases down a group.
- The further the valence electron shell is from the nucleus of an atom, the weaker the pull of the atom on the electrons in a bonding pair.
\(\rightarrow\) Noble gases have a complete valence shell, so they do not attract electrons.
- Lanthanides and actinides (the two rows of elements below the main table) have complicated and weird chemistry, so they will not follow any trends.
- There is little variance in the electronegativity values for the transition metals.

Electronegativity (metallic character)
Metallic character is a set of physical and chemical properties including reactivity, conductance, ductility, and malleability. One important characteristic is how readily an atom can lose an electron.
- Metallic character decreases across a period.
\(\rightarrow\) This is due to the increasing attraction between valence electrons and the nucleus across the period.
- Increases down a group.
\(\rightarrow\) This is because the atomic size is increasing, which causes the outer electron shells to be farther away. This decreases effective nuclear charge, making electrons more readily lost.
Ionization energy
- This is the amount of energy needed to pull an electron away from the atom in the gaseous state, or the tendency of an atom to give up electrons. This is conceptually the opposite of electron affinity.
- There is an ionization energy measured for every electron in an atom. The first ionization energy is the amount of energy required to remove the first electron. The second ionization energy is the amount required to remove the second, and so on.
- A factor that affects ionization energy is electron shielding. This is the shielding of the valence electrons from the nucleus by the inner electrons.
- Trends in first ionization energy ONLY
- Increases from left to right across a period.
\(\rightarrow\) This is due to increasing effective nuclear charge.
- Decreases from top to bottom down a group
\(\rightarrow\) Because of electron shielding.
- The noble gases have very high first ionization energy.
\(\rightarrow\) They have full valence shells.
- Increases from left to right across a period.

Electron affinity
- Electron affinity is the ability of an atom to accept an electron. This is a quantitative measurement of the energy change occurring when an electron is added to a neutral gas atom. For more information, visit a tutor. All appointments are available in person at the Student Success Center, located in the library, or online.
- Like ionization energy, there is an electron affinity measured for an atom for each successive electron added.
- Trends in first electron affinity
- Tend to be negative, meaning energy is released when the electron is added.
- The amount of energy released increases from left to right across a period.
- The amount of energy released decreases down a group.
- The noble gases have positive first electron affinities, meaning they require energy to accept an electron.

Atomic radius
The atomic radius is one-half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms of the same element.
- Increases right to left (backwards) across a period.
\(\rightarrow\) Electrons are added left to right across a period to the same valence shell. Simultaneously, positive protons are added to the nucleus. The effect of the positive protons is greater than the negative electrons, so there is a higher effective nuclear charge. The nucleus attracts the electrons more strongly, decreasing the atomic radius.
- Increases down a group.
\(\rightarrow\) Valence electrons are added to shells further away from the nucleus. As shells are added, the outer electrons are shielded from nuclear attraction from the inner electrons via electron shielding.

Metallic character
Metallic character is a set of physical and chemical properties including reactivity, conductance, ductility, and malleability. One important characteristic is how readily an atom can lose an electron.
- Metallic character decreases across a period.
\(\rightarrow\) This is due to the increasing attraction between valence electrons and the nucleus across the period.
- Increases down a group.
\(\rightarrow\) This is because the atomic size is increasing, which causes the outer electron shells to be farther away. This decreases effective nuclear charge, making electrons more readily lost.

Melting points
The melting point is the amount of energy required to break a bond(s) to change the solid phase of a substance to a liquid. Generally, the stronger the bond between the atoms of an element, the more energy required to break that bond. Because temperature is directly proportional to energy, a high bond dissociation energy correlates to a high temperature. Melting points are varied and do not generally form a distinguishable trend across the periodic table. However, certain conclusions can be drawn from the figure.
- Metals generally possess a high melting point.
- Most non-metals possess low melting points.
- The non-metal carbon possesses the highest melting point of all the elements. The semi-metal boron also possesses a high melting point.

Summary
Written by Fillios Memtsoudis