Macromolecules vs micromolecules:
- Macromolecules are large chain-like molecules formed by similar/identical covalently bonded smaller molecules which have their own function. Large chain-like molecules are also known as polymers.
- Micromolecules are monomers (building blocks for polymers). For example, amino acids (monomers) link together to form proteins (polymers).
Reactions that polymers are part of:
- Condensation/synthesis reaction → Covalent bonding of two molecules (either two monomers or a monomer and polymer). If the reaction produces water molecules it is known as a dehydration reaction.
- Breakdown of polymers occurs by disassembling the polymer to monomers. If the reaction requires water as a reactant, then it's called hydrolysis (breakdown with water).
Classes of macromolecules:
- Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) are made of nucleotide monomers.
- Carbohydrates (saccharides) are made of monosaccharides.
- Proteins are building blocks made of amino acids.
- Lipids are building blocks made of fatty acids. Their structure is determined by the monosaccharides and position of glycosidic linkages.
Carbohydrates (saccharides)
Monosaccharides
- General chemical formula: CH2O
- Monosaccharides traits include having a carbonyl and hydroxyl group.
- Classification based on length of carbon skeleton (ranging between 3 and 7 carbons).
- Source of diversity being the spatial arrangement around asymmetric carbons (a carbon attached to four different atoms or groups of atoms).
- Most five- and six-carbon sugars are more stable under physiological conditions when in ring form.
Polymers of sugars (dissacharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides)
- Dissacharides are simply two monomers together (e.g. maltose = glucose + glucose); and oligosaccharides are made of 3-10 monomers; polysaccharides have more than 10 monomers.
- The monomers are joined by a glycosidic linkage (a covalent bond formed by a dehydration reaction, where glyco- purely refers to carbohydrate).
- Functions of Polymers (Cellulose vs vs Chitin vs Glucose vs Starch)
- Stach and glycogen are mainly used for energy storage while Cellulose and chitin are primarily used for structural support. They are all made of glucose monomers, but chitin also contains nitrogen.
- In plants: Starch stores energy while cellulose provides structural support in cell walls.
- In animals: glycogen stores energy while chitin is structural (mainly in the exoskeleton of arthropods).
- Starch can be found in two forms: amylopectin and amylose. Amylopectin is branched while amylose is linear. They are both digestible.
- Cellulose Cellulose molecules are never branched, so some hydroxyl groups on the glucose monomers are free to hydrogen-bond with hydroxyl groups from other cellulose molecules, allowing parallel alignment of the molecules, therefore making it indigestible for almost all animals, including humans.
- Ruminants (e.g. cows) CAN digest cellulose, but only because they contain specific enzymes to break them down. They release methane in the process.
- Chitin is found in the exoskeletons of arthopods (e.g. insects) and fungi. It is generally insoluble.
Lipids
- Because they mostly consist of non-polar C-H bonds, they are hydrophobic meaning they don't mix with water well, if at all.
- This group does not include true polymers, lipids are generally not big enough to be considered macromolecules.
- The monomers of lipids are fatty acids.
- Structure
- The carbon skeleton consists of usually 16-18 carbon atoms, where the carbon at one end of the skeleton is part of a carboxyl group and the rest of the skeleton is made up of a hydrocarbon chain. The relatively non-polar covalent bonds between carbon and hydrogen in the hydrocarbon chain are the reason why fats are hydrophobic.
- Types
- The type of the fat is the result of the type of the composing fatty acids, so we can't have saturated and unsaturated fats if there aren't saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
- The term "saturated" refers to the saturation of hydrogen atoms in the hydrocarbon chain.
- Unsaturated fatty acids have more double-bonded carbons, therefore nearly always having a kink in the hydrocarbon chain due to the cis double bond.
- Most animal fats are saturated and the flexibility of the molecules allows them to pack together tightly, therefore they are solid at room temperature.
- As opposed to animal fats, plant and fish fats are generally unsaturated, with their kinks preventing them from packing together lightly, so they are referred to as oils.
- The heavy consumption of saturated fats is linked to cardiovascular diseases. In the process of hydrogenating fats (adding hydrogen so they can become solid) there can occur unsaturated fats with trans double bonds, aka trans fats, that can contribute to coronary heart disease.
- Categories of Lipids
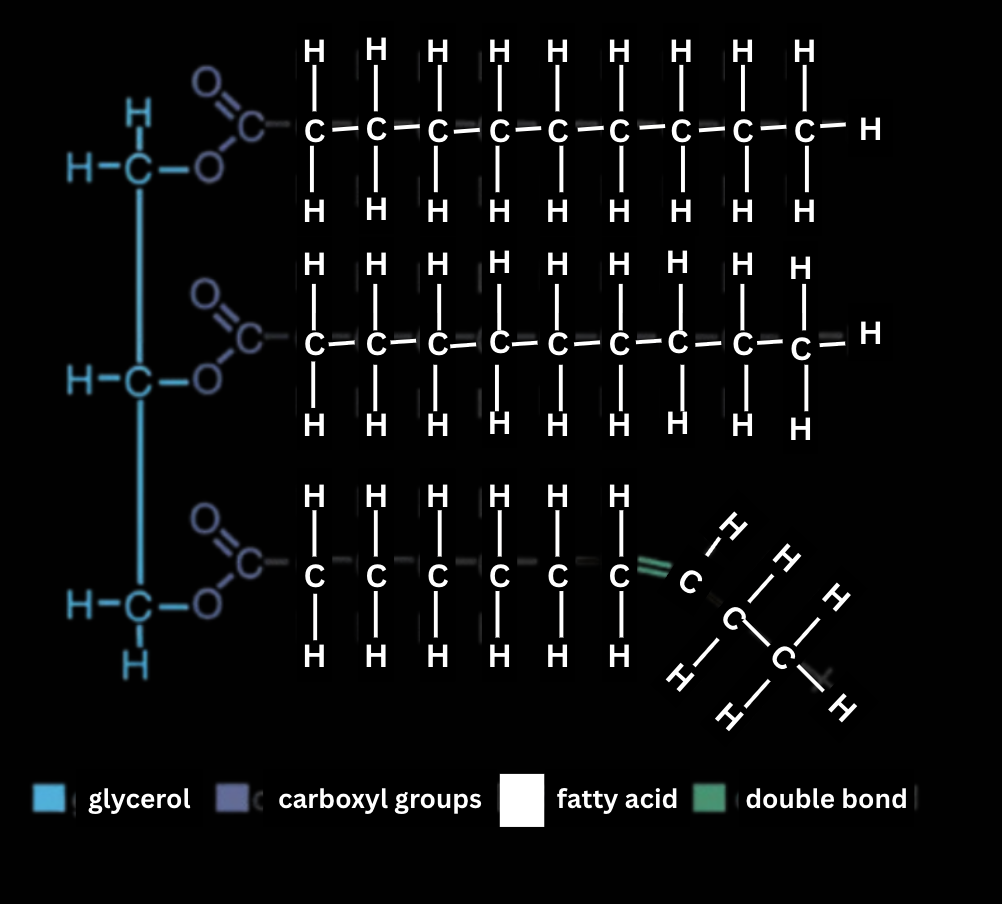
- Fats → assembled from smaller molecules (a glycerol and three fatty acids, also called triglycerides or triacylglycerols because of this) by dehydration reactions.
- Since fat molecules store more energy than polysaccharides, animals store extra energy in their adipose tissue which can act as a cushion for vital organs and help with thermal insulation.
- Phospholipids
- Because phospholipids make up a major part of cell membranes, they are vital for cells. Phospholipids are smaller than fats with there being two fatty acids attached to a glycerol where the third hydroxyl group of glycerol is attached to a phosphate group, which has negative electrical charge.
- This allows for different behavior of the different ends of the phospholipid (the head (glycerol + phosphate group) is hydrophilic and the tails (the fatty acids hydrocarbon skeletons) are hydrophobic) thus forming a "bilayer" when in an aquatic environment (2 layers of phospholipid molecules with their tails on the inside and heads on the outside) and for smaller charged or polar molecules to attach to the phosphate group.
- SteroidsSteroids - lipids distinguished by a carbon skeleton with four fused rings, differentiated by the particular chemical group attached to this ensemble of rings. cholesterol is a steroid molecule with a crucial role in animal life such as being a common component of animal cell membranes and a precursor from which other steroids are synthesized. Even though some researchers have doubts, it is highly speculated that cholesterol can contribute to atherosclerosis.
Proteins
- Definition: a protein is a biologically functional molecule made up of one or more polypeptides, each folded and coiled into a specific three-dimensional shape. They make up more than 50% of cell dry mass, act as catalysts by speeding up chemical reactions in the cell while not being consumed in the reaction, called enzymes, or play major roles in defense, storage, transport, cellular communication, movement or structural support.
- To Note!The terms polypeptide and protein aren't synonymous! polypeptide refers only to the chain of amino acids, while a protein is a functional molecule, consisting of one or more specifically tangled polypeptides.
- Structure:They are a very diverse group of molecules and are thought to be the most structurally sophisticated molecules. The monomers of proteins are amino acids. There are 20 amino acids, each slightly different from the other.
- Amino Acids:
- Amino acids (building blocks of proteins). There are 20 different kinds of amino acids.
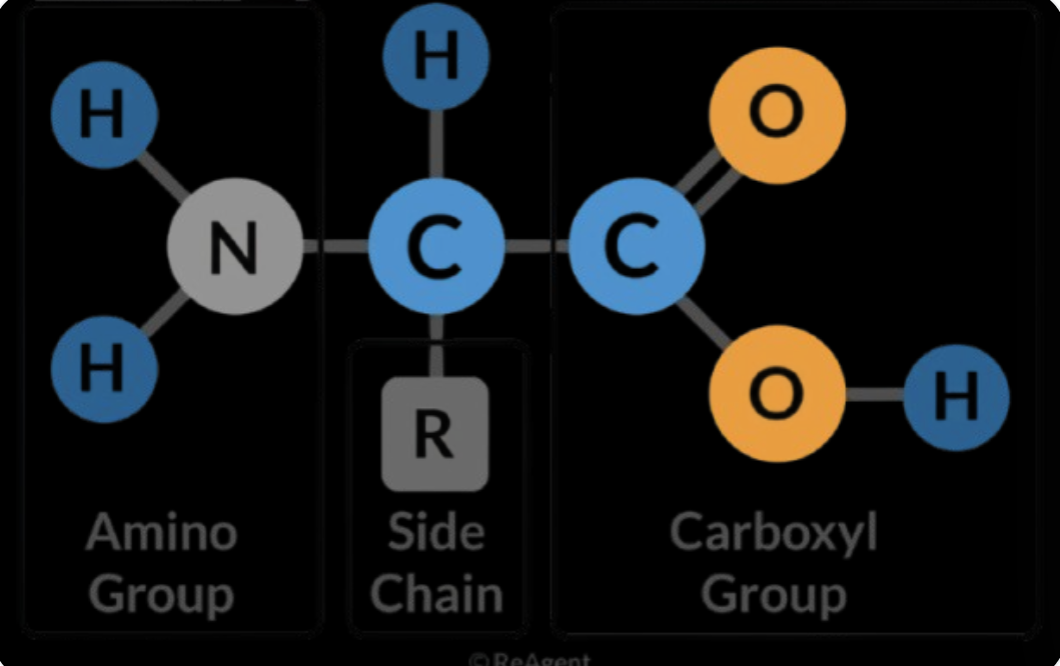
- Amino group (NH2) - ionizes in cellular pH; Alpha carbon atom (the central carbon atom to which all the other parts are bonded to); carboxyl group (-COOH) - also ionizes, making the whole amino acid usually ionized in physiological pH; and R group (determines the identity, with that, the structure and the behavior of the amino acid). It can be a simple group or a large carbon chain, can be hydrophilic (polar), hydrophobic (non-polar) or entirely ionized (either acidic or basic).
- Bonded by peptide bonds, so a polymer of amino acids is called a polypeptide. The chain of peptides without their R-groups is regarded as the polypeptide backbone. The properties of the polypeptide are entirely dependent on the kind and sequence of side chains.
- The structure determines the proteins structure (this can be seen in antigen-antibody interactions as well as in receptor binding of active substances such as hormones, drugs, etc. where the binding of the molecules is very specific, kind of like a handshake).
- Primary Structure- The sequence of amino acids, which is determined by inherited genetic information (you will learn more about how a protein is made in gene transcription). The primary structure dictates the secondary and tertiary structure, as the chemical interactions between the amino acids determine the folding of the backbone.
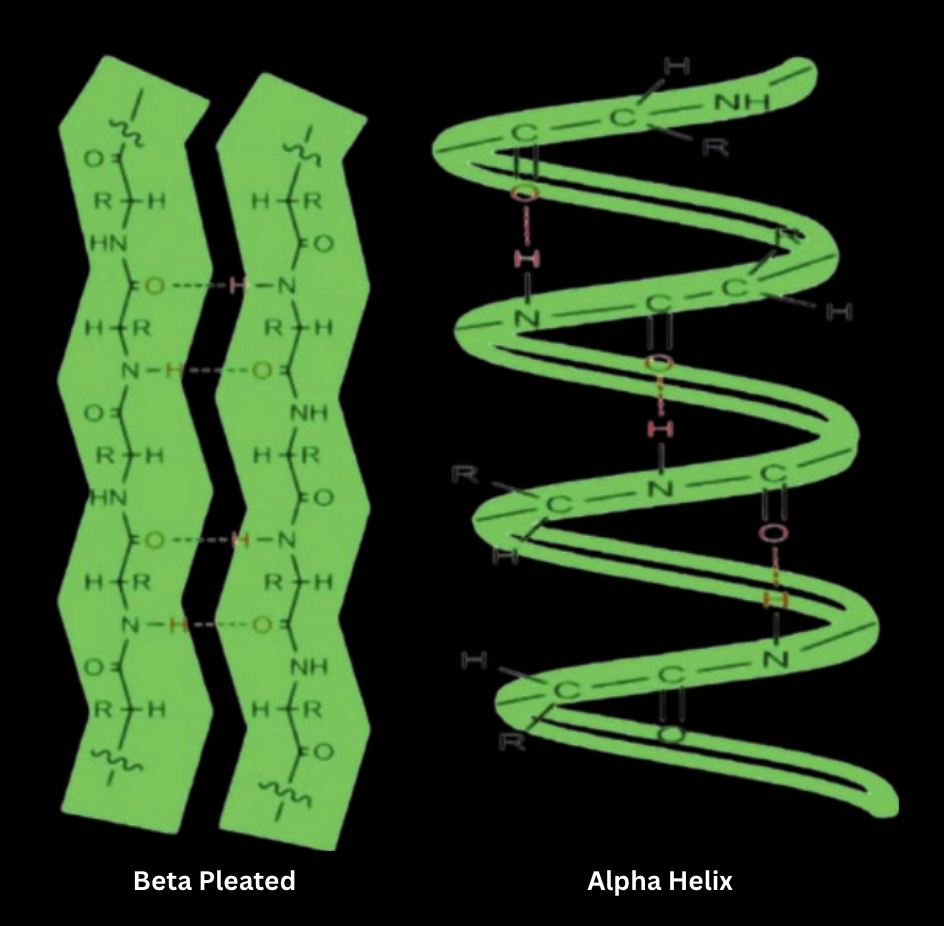
- Secondary Structure- The coils and folds of the polypeptide chain as a result of hydrogen bonding between the repeating parts of the amino acid backbone. Examples of secondary structures are the alpha helix, which is a delicate coil held together by H-bonds between every fourth amino acid, and the beta pleated sheet, which refers to the structure where two or more segments of the polypeptide chain lying side by side (a.k.a. beta strands) are connected by hydrogen bonds between parts of the beta strands. Helixes are found in globular (circular of sorts) proteins as multiple stretches separated by non helical regions and in fibrous (shaped more like strands) proteins such as alpha keratin (the protein hair is made from), they are found over most of the length of the protein. Pleated sheets make up the core of many globular proteins, and make up most of the structure of some fibrous proteins, including the silk protein of a spider's web.
- Tertiary Structure- The overall shape of the polypeptide as a result of the chemical interactions between the side chains of the amino acids constituting the backbone. An example of such interaction is called a hydrophobic interaction, where the amino acids with hydrophobic side chains end up in clusters at the core of the protein, a side effect of the van der Waals interactions, due to contact with water. Disulfide bridges (a type of covalent bond), by covalently bonding sulfhydryl groups (-SH) and forming a bridge of two sulfurs (-S-S-).
- Quaternary Structure- The overall protein structure that results from the aggregation of the polypeptide subunits. Such proteins are collagen, hemoglobin and transthyretin. What determines the protein's structure? For the most part, the answer is the amino acid sequence, because the three-dimensional shape is determined by the chemical interactions between the amino acids. The folding occurs as the protein is being synthesized in the crowded environment of the cell, aided by other proteins. Otherwise, it depends on the proteins chemical and physical environment, factors such as the pH, salt concentration, temperature, etc. the process in which the protein loses its shape, with that, its function is called denaturation. Denaturation can occur when the polarity of the solvent is changed, there are chemicals which can loosen the bonds between the amino acids, etc.
Nucleic Acids
- FunctionRNA (ribonucleic acid) and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) are polymers made up of monomers called nucleotides. Genes, which are basic units of heredity, molecularly represented by sequences of nucleotides, code for the amino acid sequences of proteins, which makes them very important as molecules, entirely. Both molecules work together to make gene expression possible. DNA provides directions for its own and RNA replication, where it directly controls protein synthesis.
- Nucleotides- the building particles of nucleic acids.vThe polymers formed from nucleotides are called polynucleotides. The components of the nucleotide are as follows:
- A nitrogenous base- it attaches to the sugar, contains carbon and nitrogen, called a base because of the amino group that can bond an extra H atom. There are 5 total possible nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine(C), thymine (T) and uracil (U). Based on the number of carbon-nitrogen rings (either 1 or 2), the nitrogenous bases can be classified as purines, nitrogenous bases with 2 carbon-nitrogen rings (A and G), and pyrimidines, nitrogenous bases with a single carbon-nitrogen ring (C, T, and U).
- A pentose (check carbohydrates part) - in DNA, the pentose sugar is deoxyribose (hence the name of DNA), while in RNA, ribose is the pentose sugar present. The difference between deoxyribose and ribose is the presence of the -OH group in ribose and a -H atom in deoxyribose on the second carbon. (check img).
- A Phosphate Group- the part of the nucleotide that allows it to bond with another nucleotide to form the string-like molecule, or more precisely, the sugar-phosphate backbone. The phosphate group is attached to the hydroxyl group of the 5' carbon of one sugar and the hydroxyl group of the 3' carbon of the sugar of the next nucleotide, therefore forming a 5'3' phosphodiester linkage. This bond is not formed by a simple dehydration reaction like the other linkages connecting monomers in macromolecules because in order to be broken, two phosphate groups have to be removed. The end where the phosphate group from the 5' sugar is located is called the 5' end, while the other end is called the 3' end. When writing out the sequence, the way of writing it is such that it starts from the 5' end and ends at the 3' end. ex. 5'-CGCTTTAAC-3.
- DNA is the genetic material that organisms inherit from their parents. The DNA molecules are safely stored in the nucleus, where one chromosome is made from one single strand of DNA containing several hundred or more genes. When cell division occurs, the DNA molecules replicate and the genetic information is passed down from mother to daughter cell. The cell's activity and components are all determined by DNA, but the activity is executed mostly by proteins in the cell.
- The structure of DNA is a double helix, there the two strands are antiparallel (one strand is positioned in the 5'->3' direction, the other one in the 3'->5' direction), where the two sides are complementary, meaning that the nucleotides have formed a base pair (A pairs up with T, C pairs with G). This feature enables making another copy of the exact DNA molecule when cell division occurs.
- RNA, on the other hand, is kind of like DNA's helper. The entire gene expression process goes something like DNA->RNA->protein, where the type of RNA used is called messenger RNA (mRNA). The sites of protein synthesis are the ribosomes, which are located outside the nucleus, in the cytoplasm, so mRNA has to deliver the genetic information from the DNA to the ribosomes.
- RNA, unlike DNA, is single-stranded, so it takes the three-dimensional shape which is needed for its function, where base pairing can occur between two regions of the same or two different molecules. The base pairing is different in RNA, A pairs with U, C pairs with G.
- The main differences between RNA and DNA are listed in the table below.
| Comparison | DNA | RNA |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Storage of genetic information and transmission of genetic information to offspring. | Transfer of genetic code to make proteins, storing of genetic blueprints in primitive organisms, transmission of genetic information is some organisms. |
| Structure | Double helix, longer molecule | Single strand, shorter molecule |
| Propagation | Self-replicating | Synthesized from DNA on an as-needed basis |
| Base Pairing | Adenine-thymine and guanine-cytosine | Adenine-uracil and guanine-cytosine |
| Reactivity | Stable molecule, less susceptible to enzyme attack | More reactive than DNA, not stable in alkaline conditions, susceptible to enzyme attack |
| UV Damage | Susceptible to UV damage | More resistant to UV damage than DNA |
| Pentose Sugar | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
Water
Even though water isn’t an organic molecule, it’s vital for an organism's survival. Key functions of water in the cell and in tissues are:
- Thermoregulation
- Being an universal solvent
- Serving as a medium for chemical reactions
- As a component of body fluids, serves as a lubricant and shock absorber
Written by Mila Porjazoska